Peer-Reviewed Articles:
- Pandey, P.K., Pasternack, G. B., Majumdar, M., Soupir, M.L., Kaiser, M. S. (2015) A neighborhood statistics model for predicting stream pathogen indicator levels. Environment Monitoring and Assessment 187:124.
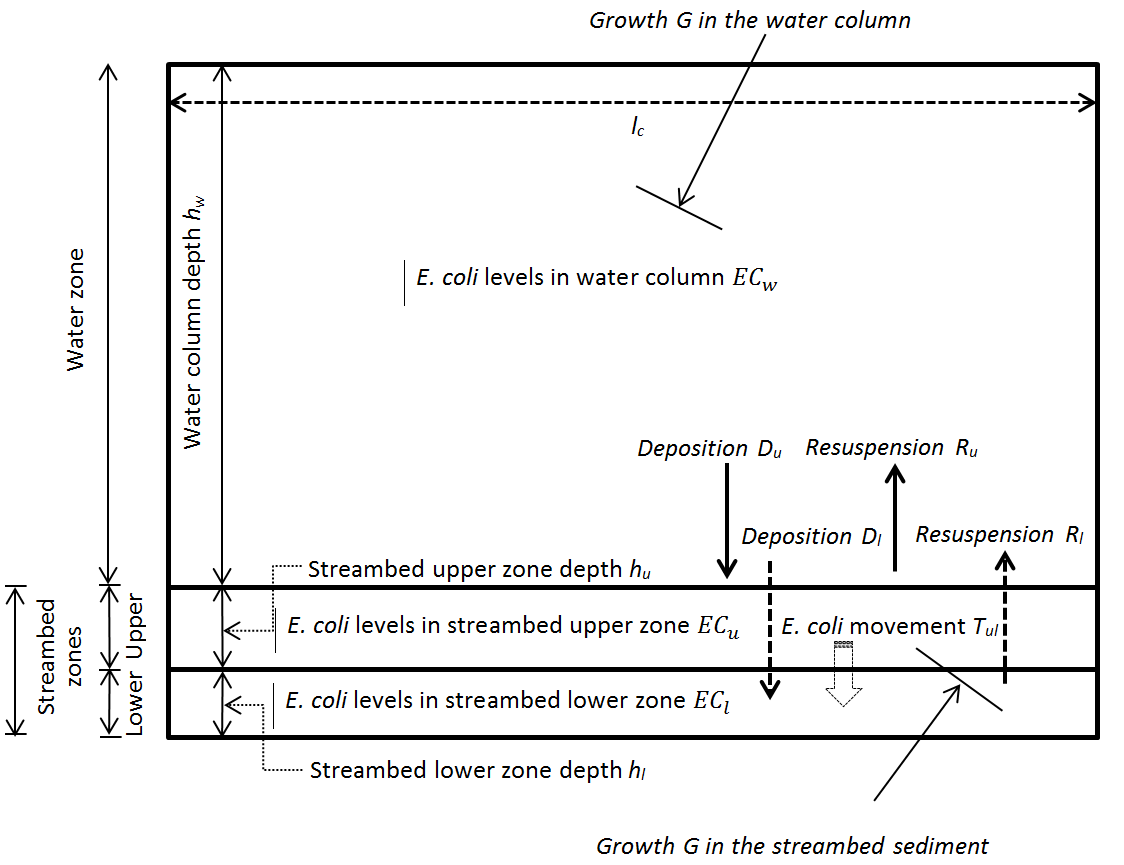
- Pandey, P.K., Soupir, M. L. (2014). Assessing linkages between E. coli levels in streambed sediment and overlying water in an agricultural watershed in Iowa during the first heavy rain event of the season. Transaction of the ASABE 57 (6): 1571-1581.
- Pandey, P.K., Kass, P. H., Soupir, M. L., Biswas, S., Singh, V. P. (2014). Contamination of water resources by pathogenic bacteria. AMB Express 4:51.
- Pandey, P.K., Soupir, M.L. Assessing the impacts of E. coli laden streambed sediment on E. coli loads over a range of flows and sediment characteristics. Journal of American Water Resources Association, DOI: 10.1111/jawr.12079.
- Pandey, P.K., M.L. Soupir, Rehmann C.R. (2012) Predicting resuspension of Escherichia coli from streambed sediments. Water Research 46(1):115-126.
- Pandey, P.K., Soupir, M.L., Haddad, M., Rothwell, J. (2012) Assessing impacts of watershed indices and precipitation on in-stream E. coli concentrations. Ecological Indicator 23(2012):641-652.
- Pandey, P.K., Soupir, M.L. (2012) Non-point source pollution. Berkshire Encyclopedia of Sustainability: Ecosystem Management and Sustainability. Berkshire Publishing Group. LLC, Great Barrington, MA, USA.

In-stream E. coli monitoring and modeling